Understanding Jaundice: A Comparative Study in Ayurveda and Allopathy
Introduction
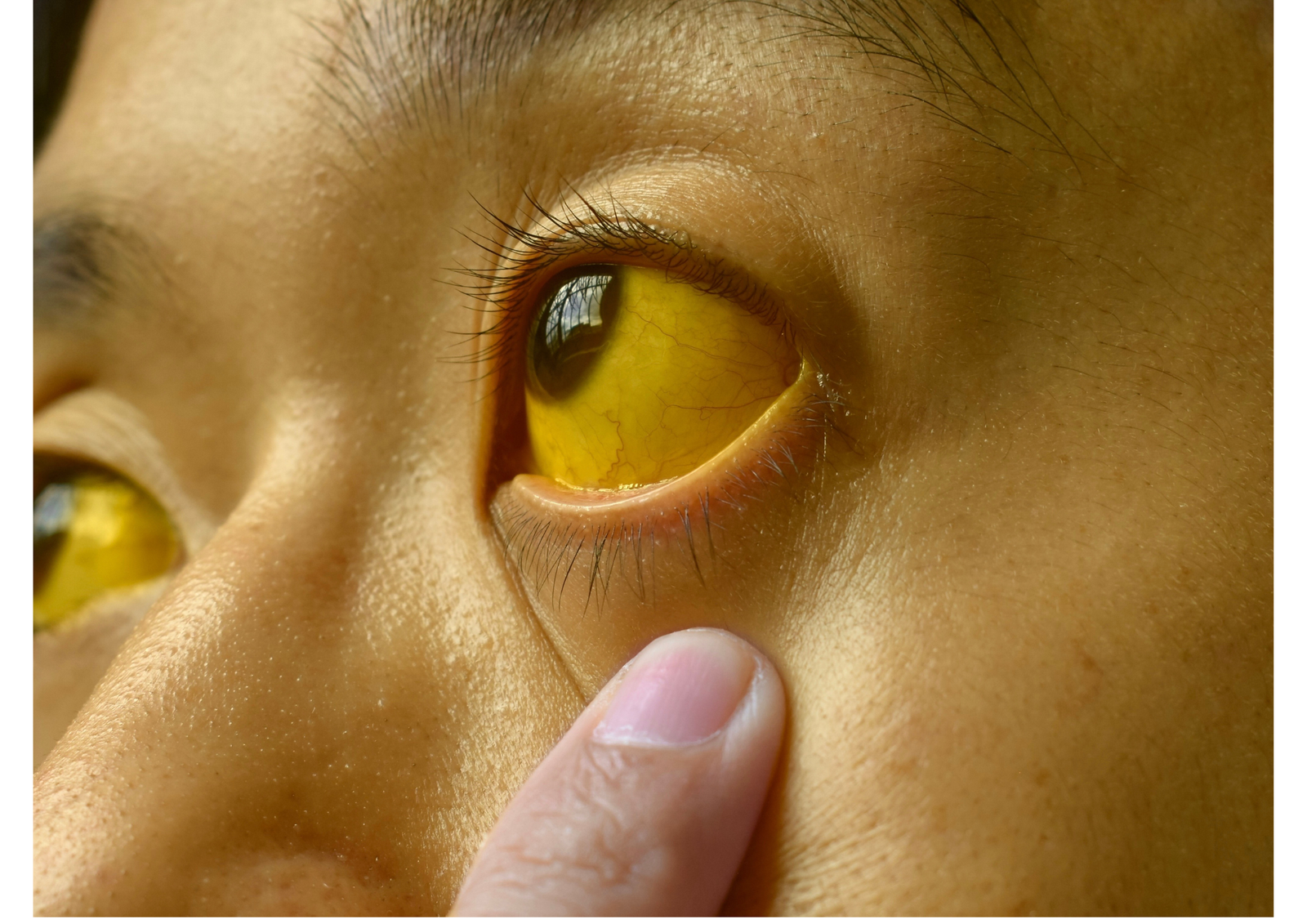
Jaundice, derived from the French word “jaune” meaning yellow, is a medical condition characterized by the yellowing of the skin, sclera (whites of the eyes), and mucous membranes due to increased levels of bilirubin in the blood. While it is not a disease itself, jaundice is a symptom of underlying liver, gallbladder, or pancreatic issues.
In both Ayurveda and Allopathy, jaundice is approached with distinct diagnostic methods and treatment principles. This blog aims to explore jaundice through both perspectives—integrating the time-tested holistic methods of Ayurveda and the advanced diagnostics and pharmacology of Allopathy.
Section 1: Understanding Jaundice in Modern Medicine (Allopathy)
1.1 Causes of Jaundice
In Allopathy, jaundice occurs due to one of three mechanisms:
- a) Pre-hepatic (Hemolytic Jaundice):
- Increased breakdown of red blood cells
- Example: Sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, malaria
- b) Hepatic (Hepatocellular Jaundice):
- Liver diseases leading to inability to process bilirubin
- Example: Hepatitis (A, B, C, etc.), cirrhosis, alcoholic liver disease
- c) Post-hepatic (Obstructive Jaundice):
- Obstruction in bile flow from the liver to the intestine
- Example: Gallstones, tumors, strictures
1.2 Signs and Symptoms
- Yellowing of skin and eyes
- Dark-colored urine
- Pale stools
- Fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abdominal pain (especially right upper quadrant)
- Itching (in obstructive cases)
1.3 Diagnosis in Allopathy
- Blood tests: Serum bilirubin (direct and indirect), liver function tests (LFTs), CBC
- Imaging: Ultrasound, CT scan, MRCP
- Liver biopsy (in chronic cases)
1.4 Treatment Approaches in Allopathy
- a) Medical Management:
- Hepatitis: Antiviral medications (e.g., interferon for Hepatitis B & C)
- Autoimmune causes: Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants
- Cholestasis or obstruction:Ursodeoxycholic acid
- b) Surgical or Interventional Procedures:
- Gallstone removal or biliary stenting
- Liver transplantation in end-stage liver failure
- c) Supportive Care:
- Adequate hydration
- Nutritional support
- Avoiding alcohol and hepatotoxic drugs
Section 2: Ayurvedic Perspective on Jaundice (Kamala)
In Ayurveda, jaundice is known as Kamala, a Pitta-dominant condition primarily associated with Yakrit (liver) dysfunction and blood impurities.
2.1 Types of Kamala in Ayurveda
Based on classical Ayurvedic texts, jaundice is classified as:
a) Shakhasrita Kamala:
- Caused by excessive Vata and Kapha blocking Pitta in peripheral tissues
- Less severe and easily curable
b) Kumbha Kamala:
- Chronic and severe jaundice (similar to obstructive or cirrhotic jaundice)
- Caused by prolonged untreated Kamala
c) PanduPurvarupa Kamala:
- Jaundice occurring as a complication of anemia (PanduRoga)
d) Halimaka:
- A rare variety involving all three doshas
- Characterized by fever, fainting, and blackish-yellow discoloration
Nidana (Causes) in Ayurveda
- Overconsumption of Pitta-aggravating foods (spicy, oily, fermented)
- Alcohol intake
- Suppression of natural urges
- Prolonged fasting or emaciation
- Excessive anger and stress
Lakshana (Symptoms)
- Peetatatwak (yellow skin)
- Peetanetra (yellow eyes)
- Peetamutra (yellow urine)
- Arochaka (loss of appetite)
- Agnimandya (poor digestion)
- Daha (burning sensation)
- Vibandha (constipation)
Samprapti (Pathogenesis)
Aggravated Pitta accumulates in the liver and spreads into the blood and skin, causing yellow discoloration. Obstruction by Kapha or Vata can worsen the situation, resulting in more chronic or severe forms.
Ayurvedic Management of Kamala
ShodhanaChikitsa (Detoxification Therapy)
- a) Virechana (Purgation):
- Main therapy to remove excess Pitta from the liver and intestines
- Mild laxatives like Trivritchurna, Avipattikarachurna
- b) Basti (Medicated Enema):
- In cases of Vata-associated Kamala (e.g., Kumbha Kamala)
ShamanaChikitsa (Palliative Care)
- a) Herbal Formulations:
- Kutki (Picrorhizakurroa):Hepatoprotective and Pitta-pacifying
- BhumiAmla (Phyllanthusniruri): Effective in viral hepatitis
- Kalmegh (Andrographispaniculata): Bitter tonic and liver stimulant
- Sharpunkha (Tephrosiapurpurea): Useful in hepatomegaly and jaundice
- Guduchi (Tinosporacordifolia):Rasayana and immunomodulator
- b) Classical Ayurvedic Formulations:
- ArogyavardhiniVati
- PunarnavadiMandur
- Bhringarajasava
- Kumaryasava
- Liv 52 (Ayurvedic proprietary medicine)
Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations (Pathya-Apathya)
Pathya (Wholesome):
- Light, easily digestible food (moong dal, rice gruel)
- Boiled vegetables
- Coconut water, sugarcane juice (in moderation)
- Buttermilk
- Warm water with turmeric
Apathya (Avoidable):
- Fried, spicy, and oily food
- Heavy dairy products (paneer, cheese)
- Alcohol
- Stress and anger
- Daytime sleep and late-night awakening
Comparative Analysis of Ayurveda and Allopathy
| Aspect | Ayurveda | Allopathy |
| Approach | Holistic and Dosha-based | Symptom and cause-specific |
| Diagnostics | Pulse diagnosis, NadiPariksha, Dosha analysis | Blood tests, imaging, biopsy |
| Treatment | Detoxification (Panchakarma) + Herbs | Antivirals, surgery, supportive care |
| Timeframe | Gradual and long-term healing | Fast and targeted relief |
| Side Effects | Minimal when properly used | Possible (drug toxicity, side effects) |
| Preventive Measures | Strong emphasis on diet and lifestyle | Limited emphasis |
Integration of Ayurveda and Allopathy
The best results in jaundice management often come from an integrative approach:
- Acute or emergency cases: Allopathy excels in immediate diagnostics, antiviral treatment, and surgical intervention.
- Chronic liver conditions: Ayurveda offers long-term healing and regeneration with minimal toxicity.
- Recovery phase: Herbal support and Panchakarma therapies can accelerate liver repair and prevent recurrence.
- Diet and lifestyle: Ayurvedic principles of Ahara (food) and Vihara (conduct) help maintain liver health post-treatment.
Preventive Tips for Jaundice
Whether viewed from a modern or Ayurvedic lens, jaundice is largely preventable with these key lifestyle strategies:
From Allopathic Perspective
- Vaccination against Hepatitis A and B
- Safe drinking water and hygiene
- Avoid sharing needles or unprotected sex (Hep B/C prevention)
- Avoid excessive alcohol
- Regular health checkups
From Ayurvedic Perspective
- Avoid overexposure to sun, anger, and heat (Pitta aggravators)
- Regular detoxification (Virechana once or twice a year)
- Eat seasonal fruits and vegetables
- Follow Dinacharya (daily routine) and Ritucharya (seasonal routine)
- Incorporate liver-friendly herbs like turmeric, aloe vera, and amla
Get more information click here.
If you want 100% ayurvedic medicine. click here